Pediatric ear infections are very common due to their smaller eustachian tubes and underdeveloped immune system. A middle ear infection, or otitis media, occurs when the bacteria or virus causing a throat sore or upper respiratory condition spreads to the ear.
Most ear infections recover on their own within a few days; otherwise, they can be treated with antibiotics and pain medication.
Are you a new parent worried about the possible ear infection symptoms baby may have? Then this blog is just for you.
According to a 2006 statistic, 8.8 million children under the age of 18 years in the USA suffer from ear infections or otitis media [7]. Thus, becoming one of the significant key concerns for millennial parents. David Tunkel, M.D. from Johns Hopkins Medicine, states that most parents are concerned that an ear infection may affect the hearing of the child irreversibly [7].
So, we take a deeper look into what otitis media is, its causes along with signs of ear infection in toddlers, and how to prevent ear infections in babies.
What Is An Ear Infection?
An ear infection is defined as an inflammation of the middle ear that is usually caused by bacteria and occurs when there is a fluid build-up behind the eardrum.
People of all ages and gender are vulnerable to getting an ear infection; however, it is more prevalent in toddlers and babies [6].
Ear infection, in scientific or medical terms, is also called Otitis Media (OM). It is seen that 5 out of every 6 children suffer from at least one ear infection by their third birthday. It is also one of the most common reasons for parents to visit a doctor with their child [6].
How Do Ear Infections Happen?
In most cases, an ear infection is caused by bacteria. It often begins when a child has a cold, sore throat, or other upper respiratory infection. The bacteria from the upper respiratory tract may spread to the middle ear, causing an ear infection.
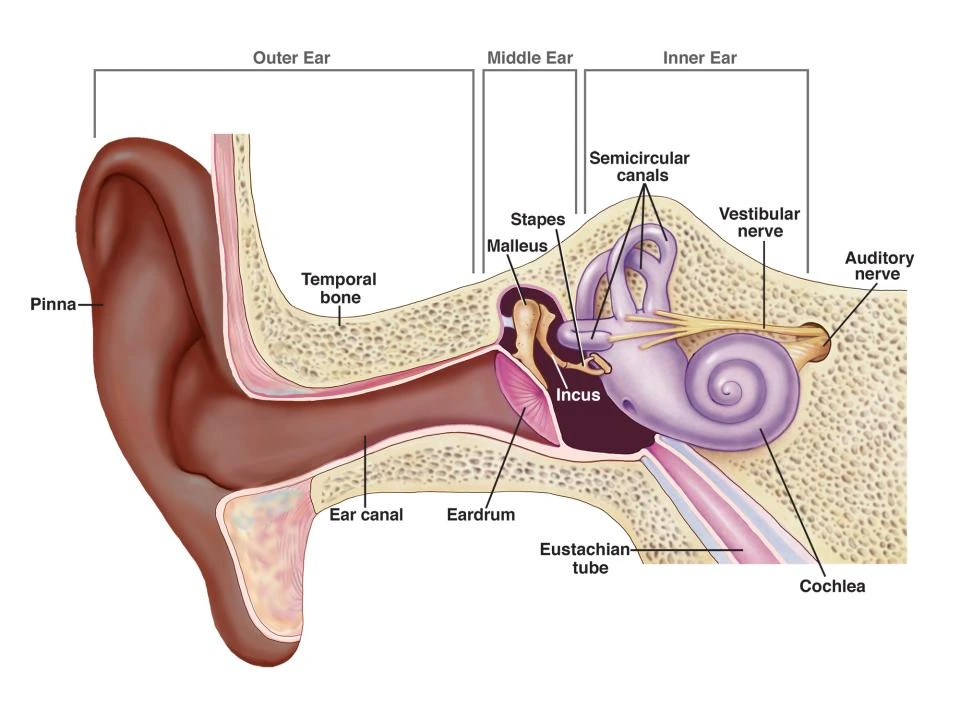
The ear has three major parts- the outer ear (pinna), the middle ear, and the inner ear.
Apart from these three core parts of the ear, other parts, such as the eustachian tube, which is a small passageway that connects the upper throat to the middle ear, may also get infected [6].
Why Are Children More Likely Than Adults To Get Ear Infections?
Some of the reasons why children are more likely to get an ear infection compared to an adult are-
-
The Eustachian tubes are smaller in children than in adults. Thus, the fluid produced by the ear infection becomes difficult to drain.
-
The immune system of a child is weaker than an adult, thus making it harder for them to fight an infection.
-
Adenoids, a small pad of tissue that is located behind the back of the nose, near the eustachian tubes, and above the throat, may respond to bacteria passing through the nose and mouth. Thus, in most cases, bacteria get trapped in these adenoids causing chronic infection [6].
How To Know If Your Baby Has An Ear Infection- Signs Of Ear Infection In Baby
In most babies, ear infections may occur before they have learned how to talk. Thus, identifying that the baby has an infection may be challenging. So, here are a few tips on how to know if your baby has an ear infection-
-
Trouble hearing
-
Fluid draining from the ear
-
Sleep issues
-
Pulling at the ear
-
Crying and Fussiness
-
Fever
-
Facing problems with balancing [6].
Signs Of Ear Infection In Toddler
There are certain symptoms of toddler ear infections. Some of them are listed below.
1. They will face difficulty in eating and sleeping.
2. Constantly rubbing their ears
3. When they cry more than usual.
4. Vomitting, dizziness, and nausea
5. Swelling or pain of the ear.
6. Constant fluid drainage from ears.
7. Fever that ranges between (105-104F) or (38-40 degree Celsius) (3).
What Are The Risk Factors For Kids Ear Infection?
Ear infections are not contagious; however, there are several risk factors for ear infections. These include:
-
Age- Children between the age group of 6 months and 2 years are more susceptible to ear infections because of the minute size and shape of their eustachian tubes.
-
Group child care- Children taken care of in group settings are more likely to get colds and ear infections than children who stay at home. Children in group settings are open to more infections, such as flu.
-
Infant feeding- Babies drinking from a bottle while lying down tend to have more ear infections than babies who are breastfed.
-
Seasonal factors- Ear infections are most effective during the fall and winter. People who deal with seasonal allergies have a greater risk of ear infections when pollen counts are high.
-
Poor air quality- Exposure to tobacco smoke or high levels of air pollution can increase the risk of ear infections.
-
Alaska Native heritage- Ear infections are more prevalent among Alaska Natives.
-
Cleft palate- People having differences in bone structure and muscles in children who have cleft palates make it more difficult for the eustachian tube to drain (1).
Diagnosis Of An Ear Infection
The physical examination of the child with the proper equipment is done by the experts. The tool that is used to view your child's eardrum is called an otoscope. After proper examination, if the eardrum is seen as red or swollen, it is a sign of an infection.
If the signs are severe in nature, another instrument called a pneumatic otoscope is used to check the fluid flow. If the fluid is inside the middle ear space, then it's a sign of an ear infection.
There are also some other diagnosis procedures followed to check the severity of the symptoms of ear infections in children. They are-
-
Tympanometry- The test is done to check fluid using air pressure.
-
Tympanocentesis- In this procedure, the fluid from the middle ear is removed by the professional who tests it for the presence of viruses or bacteria.
-
Acoustic Reflectometry- The test is done using sound waves to check the fluid.
-
Hearing tests- These tests are done by an expert called an audiologist.
Generally, ear infection symptoms are seen in children resulting in hearing loss or long-lasting effects (2).
How To Prevent Pediatric Ear Infection?
There are certain preventive measures that can be taken for the prevention of pediatric ear infections. Some of them are listed below:
-
To avoid the draining of the Eustachian tube, the baby must be put to sleep on their back.
-
You should keep your children away from secondhand smoke.
-
You, as well as the caregiver, should wash your hands frequently.
-
Breastfeeding should be provided for at least three months.
-
While feeding your baby, you should always hold the baby upwards (5).
Complications That Arise From An Ear Infection
There can be certain complications that can result from an Ear Infection. Some of the complications are listed below:
1. Mastoiditis : It is an infection of the bones present behind the ear. It can initially begin as a mild infection that can turn into something serious. Your child can develop Mastoiditis if they have repeated ear infections. Symptoms include swollen bone behind the back or redness, earlobes that are swollen, and severe headaches.
2. Hearing loss : This situation generally arises when the infections occur frequently and never really heal. The risk of hearing loss permanently is low as it is temporary in nature.
3. Facial paralysis : The nerve that animates your face runs right through the ear. As a result of the infection, the movement of one side of your face becomes impossible.
4. Meningitis : The infection occurs in the membranes that surround the brain and spinal cord. Adults and children above 2 years of age might suffer from symptoms like severe headaches, fever, and nausea. While infants might suffer extreme stiffness in the body and neck, due to which they might cry constantly.
5. Brain Abscess : when puss gathers in the brain due to long-term infection. This is more often seen in countries where access to health care is rare. Reflection of symptoms such as fever, nausea, severe headaches, etc.
6. Ruptured ear-drum : Due to the pressure of fluid building in the middle ear, there leads to a formation of a small hole. This results in bursting out of the ear drum. As stated by Dr. Chandrasekhar, ruptured ear drum heals in their own way (4).
Ear Infection Treatment For Kids
Ear infection treatment for kids depends on certain factors, such as:
-
Age of the child.
-
The severity of the infection.
-
Nature of the infection.
-
The time period of the fluid remains.
It's very often that ear infections heal on their own. But in some cases, your child might require urgent treatment such as antibiotics or pain-relieving medicines.
Treatments Based on Age
Ear Infection In Newborn - Under 6 Months :
Newborn infants under the age of 6 months almost always receive antibiotics. At this age, they are not fully vaccinated, and they require additional immunity in the form of antibiotics to fight the infection.
Six months to 2 years :
The American Academy of Pediatrics (AAP) recommends making a share decision by parents and doctors on whether to treat ear infections that are not severe in kids between the age of 6 months to 2 years. In such cases, it is often advised to watch the kid for two to three days before prescribing any antibiotic.
Over 2 Years :
In children over 2 years, ear infections are likely to clear on their own. However, for pain associated with the infection can be treated with over-the-counter medications such as acetaminophen or ibuprofen.
Other Treatment Options
Ear tubes (tympanostomy tubes) :
If your child is experiencing frequent infections, then they require ear tubes. An ear, nose, and throat (ENT) specialist puts the tubes during a process called tympanostomy. It’s an approximately 10-minute procedure. During the process, a provider inserts a small metal or plastic tube into a tiny incision (cut) in your child’s eardrum. The procedure to pierce a hole and drain the eardrum is called a myringotomy. Once the tubes are in place in position, they let air into the middle ear and allow fluid to drain (2).
Nootropics :
An inner ear infection may result in symptoms that may often cause forgetfulness, memory issues, and confusion [8]. These symptoms may be improved by the use of Modalert, which is a brand drug of Modafinil.
The use of Modalert 200 mg helps in the secretion of hormones such as dopamine, histamine, and serotonin, which helps in improving the cognitive functioning of the person. However, a physician advices people to get Modalert 200 for patients over 17 years. Infants and people below 17 years are only recommended the Nootropic after a thorough evaluation of the condition.
Antibiotics For Ear Infection Baby :
Your child may require antibiotics if the infection is caused by Bacteria. Experts may wait up to three days before prescribing antibiotics to see if a mild infection heals on its own. The need for Antibiotics increases depending on the severity of the infection.
How Long Will It Take My Child To Get Better?
Infant ear infection symptoms can be treated effectively. The child should begin to recover and start feeling better within a few days after visiting a doctor.
Once the infection clears, the fluid buildup in the middle ear will disappear within 3 to 6 weeks [6].
Ear Infection Symptoms In Children: The Key Takeaway
An ear infection is the most prevalent among children because their Eustachian tubes are smaller compared to adults. They generally occur because of the fluid that cannot drain properly, which results in muffled hearing.
Ear infections in newborns, toddlers, or children are not severe and often recover within a few days with the right treatment. Looks for signs such as fever, constant crying, imbalance, improper sleep, and flow of fluid from the ear to identify Otitis Media in children. Visit a doctor who can design the best treatment option for your child based on their age, condition, and severity.




 0
0


 May 26, 2022
May 26, 2022  By
By 




